The Multicore Association’s (MCA) Multicore Task Management API (MTAPI) is one of a number of open-source application programming interfaces (APIs) from the MCA. This includes the Open Asymmetric Multi Processing (OpenAMP) framework, which can work with platforms from Linux to bare-metal solutions. It’s applicable to almost any embedded system, including those targeting the Internet of Things (IoT).
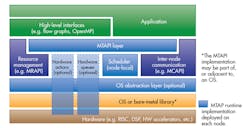
The MTAPI (Fig. 1)—a C-language API designed for low-level, lightweight task management—has the ability to address both homogeneous and heterogeneous multicore platforms. MTAPI can be used on top of RTOS and bare-metal implementations.
1. The MTAPI is a C-language application programming interface designed for low-level, lightweight task management.
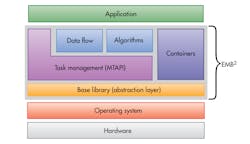
Embedded Multicore Building Blocks (EMB2) is a C/C++ library designed for the development of parallel applications. EMB2 can take advantage of MTAPI (Fig. 2), exposing the API as well as building additional functionality on top of it. These layers abstract the underlying hardware and operating system, facilitating application portability as well as providing a standard development target for designers.
Developers who use MTAPI can now exploit the added capabilities of EMB2. EMB2 allows for creation of solutions that can take advantage of EMB2 plugins like OpenCL, CUDA, and distributed systems network communication to target different hardware from CPUs to FGPAs and GPUs. As a result, developers are able to utilize hardware acceleration using a standard platform while reducing development effort.
2. Embedded Multicore Building Blocks, or EMB2, can now build on MTAPI.
“We observe an increasing need for high compute capabilities where the data is generated, primarily on the devices,” says Tobias Schüle, a member of Siemens Corporate Technology and primary creator of EMB². “This way, sensitive information can be kept secure and network traffic is reduced compared to pure cloud-based solutions. In fact, low latency is often essential in industrial applications.”
EMB2 provides basic parallel algorithms and concurrent data structures. Stream processing support includes skeleton code that enables creation of applications on top of the framework. EMB2 generally employs a non-blocking approach. It tends to avoid design pitfalls like lock contention, deadlocks, and priority inversion.
EMB2 is available on Github. The EMB2 is covered by a BSD 2-clause license, while MTAPI has a BSD 3-clause license.