Physicists make graphene discovery that could help develop superconductors
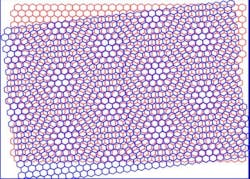
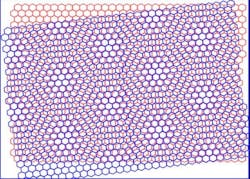
NEW BRUNSICK, NJ—When two mesh screens are overlaid, beautiful patterns appear when one screen is offset. These “moiré patterns” have long intrigued artists, scientists and mathematicians and have found applications in printing, fashion and banknotes.
Now, a Rutgers-led team has paved the way to solving one of the most enduring mysteries in materials physics by discovering that in the presence of a moiré pattern in graphene, electrons organize themselves into stripes, like soldiers in formation.
“Our findings provide an essential clue to the mystery connecting a form of graphene, called twisted bilayer graphene, to superconductors that could work at room temperature,” said senior author Eva Y. Andrei, Board of Governors professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy in the School of Arts and Sciences at Rutgers University–New Brunswick.
Graphene—an atomically thin layer of the graphite used in pencils – is a mesh made of carbon atoms that looks like a honeycomb. It’s a great conductor of electricity and much stronger than steel.
In 2010, Andrei’s team discovered that in addition to being pretty, moiré patterns formed with twisted bilayer graphene have a dramatic effect on the electronic properties of the material. This is because the moiré pattern slows down the electrons that conduct electricity in graphene and zip past each other at great speeds.
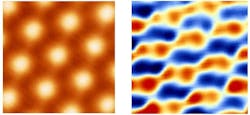
Using a technique invented by Andrei’s group to study twisted bilayer graphene, the team discovered a state where the electrons organize themselves into stripes that are robust and difficult to break.
“Our team found a close resemblance between this feature and similar observations in high-temperature superconductors, providing new evidence of the deep link underlying these systems and opening the way to unraveling their enduring mystery,” Andrei said.
The lead author is Rutgers post-doc Yuhang Jiang. Rutgers co-authors include post-doc Jinhai Mao, graduate student Xinyuan Lai and Professor Kristjan Haule. Scientists at the National Institute for Materials Science in Japan contributed to the study.