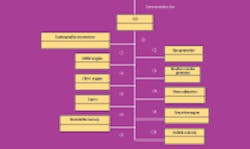
Trusted Platform Module
One key aspect NIST will address in the next steps toward the Smart Grid revolves around security. As part of the cyber security strategy, the document states, “Cyber security must address not only deliberate attacks, such as from disgruntled employees, industrial espionage, and terrorists, but also inadvertent compromises of the information infrastructure due to user errors, equipment failures, and natural disasters.”
Similar to other technology considerations, standards-based technologies are preferred. According to Brian Berger, director and marketing chair for the Trusted Computing Group (TCG), and executive vice president, marketing and sales at Wave Systems Corp., these concerns mirror those for enterprise security, which has been on TCG’s radar for several years.
The not-for-profit TCG develops open security standards for the enterprise. This includes the extension to the cloud-computing environment that could be a part of the Smart Grid communication solution. TCG’s efforts are based on a hardware device developed to provide increased security over software-only approaches. Software approaches not only reduce the processing time, they’re also subject to being overridden by the same malicious software they try to block.
Established for more than eight years, TCG’s Trusted Platform Module (TPM) specification (see the figure) is available from several semiconductor suppliers, including Atmel, Broadcom, Infineon, and STMicroelectronics. The TPM, typically a microcontroller (MCU), has been installed in over 200 million enterprise-level computers. This widespread usage makes it a well-established candidate for Smart Grid applications.
In addition to the TPM, TCG designed a network security specification called the Trusted Network Connect (TNC) for safely connecting user-centric devices such as desktop and portable computers, wireless cell phones, and PDAs to the enterprise network. A recently developed interface that performs security monitoring and classifying through a metadata access point (MAP), called IF-MAP, addresses the real-time access by unmanaged endpoints.
Endpoints—machine-to-machine connections that are traditionally difficult to authenticate to the network—include a plant’s automation and control networks, such as the utilities’ SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) networks identified in the NIST roadmap.
The Trusted Platform Module consists of several blocks that provide a hardware-based root of trust for secure communications.