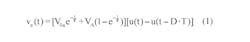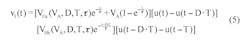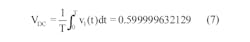This article is part of the Ideas for Design Series: Vol. 3, No. 9.
A recent Idea for Design showed a graphical technique for determining the output of an RC filter driven by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) pulse train.1 It requires the manipulation of infinite series with a limit. Therefore, it does not yield steady-state results with confidence.
Related Articles
- Graphically Determine The Output Signal Level Of An RC Filter
- Passive RC Filters Afford Low Cost And High Selectivity
- R-C Twin-Tee Circuit Reduces Power-Supply Hum
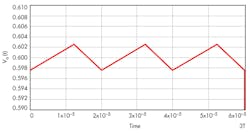
A better approach uses the concept of continuity of states and steady-state “wrap-around” to eliminate this shortcoming, since current and voltage values in a real circuit cannot change instantaneously. Current and voltage are variables with continuous values in time, from moment to moment. For a circuit structure that is switched periodically among several states repeatedly, the end state of one structure serves as the starting state of the next.
Using the same RC filter, periodic-input pulse train, and designations as the referenced Idea for Design, Equation 1 shows the filter output when the driving source VA is non-zero:
The approach presented here gives the true steady-state output in compact, closed form with a high degree of confidence. The technique can be extended to other second- and higher-order circuits that are switched periodically among multiple states.2, 3
References
1. “Graphically Determine The Output Signal Level Of An RC Filter,” Electronic Design, Oct. 3, 2013.
2. Switch-mode Power Converters, Keng Wu, Elsevier, 2005, ISBN 13:978-0-12-088795.
3. Power Rectifiers, Inverters, and Converters, Keng Wu, Lulu.com, 2008, ISBN 978-1-4357-2023-7.
Keng C. Wu has a BS from Chiaotung University, Taiwan, and an MS from Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill. He has published four books and holds seven U.S. patents. He can be reached at [email protected].
About the Author
Keng Wu
Keng C. Wu, a power electronics consultant, has published five books on power processing, was awarded “Author of the Year” twice (2003 and 2006 Lockheed Martin), and presented a 3-hour educational seminar IEEE APEC-2007 S17. He has held more than a dozen U.S. patents. He earned a BS from Chiaotung University, Taiwan, and an MS from Northwestern University, Evanston, Ill.