2026 Ethernet Forecast: Full Speed Ahead
What you'll learn:
- What’s driving the need for higher Ethernet speeds, and how the industry is responding.
- An overview of the 2026 Ethernet Roadmap that showcases near-term innovation and long-term interoperability.
- The robustness of Ethernet technology for multiple applications.
In 2026, Ethernet’s trajectory will be influenced by AI, rapid progress in standards and signaling technology, and its continued move into markets and applications beyond the data center. The convergence of these three factors suggests a time of expansion and innovation unlike any seen before. What follows explores how these forces will shape Ethernet throughout 2026.
Escalating Ethernet
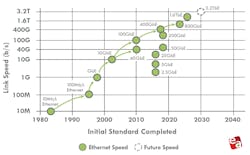
It should come as no surprise that Ethernet development continues to accelerate at an unheard-of rate. Even though IEEE 802.3 is still refining 200G/lane signaling specifications, consensus building around 400G/lane is well underway. What once felt like long-term planning is now happening in parallel.
With this exponential advancement, Ethernet has overtaken other interconnect technologies like Infiniband, making it the leader in "scale-out" AI networking. Connecting key AI functional blocks demands reliable, scalable, and interoperable products sourced from a broad and competitive market. Luckily, that openness and interoperability are at the heart of Ethernet’s value proposition.
But the high-profile, high-speed hyperscale market is only the tip of the Ethernet iceberg. Momentum is building behind widely supported initiatives such as UA Link, Ultra Ethernet, and OCP's SUE-T and ESUN projects, fueling the world’s unrelenting appetite for faster speeds. Add in the phenomenal proliferation of IoT devices — each with its own wired or wireless connection — across enterprise, industrial, and edge environments, and you’ve got the urgent need for an even more stable, predictable, and resilient Ethernet ecosystem.
Despite the swift pace of Ethernet standards development, the hyperscale market is moving forward in advance of ratified global standards. As revealed during the Ethernet Alliance’s recent Technology Exploration Forum 2025 (TEF 2025): Ethernet for AI, there’s a near-insatiable demand for high-speed, low-latency interconnects that can support booming AI and ML compute workloads.
Hyperscalers will persist in actively pursuing customized solutions for intra-data-center optimization. However, interconnects spanning disparate physical locations will continue to rely on a robust catalog of stable, interoperable standards-based solutions.
The Ethernet Alliance 2026 Ethernet Roadmap illustrates the balance between near-term innovation and long-term interoperability. Instead of focusing on a single outcome, it captures how the ecosystem is seeking continuous improvement in speed, reach, power efficiency, and deployment models while maintaining broad compatibility. The roadmap underscores Ethernet’s evolution not just at the hyperscale core, but across the full range of applications that increasingly depend on it.
Scaling for What Comes Next
The 2026 Ethernet forecast is simple: AI, more AI, and even more AI.
The constraints shaping Ethernet’s next phase aren’t theoretical. They’re physical, financial, and logistical:
- AI data centers and AI CPU orders are now being measured in gigawatts of power consumption.
- Leading semiconductor manufacturer TSMC estimates it can meet only a fraction of current demand for advanced-process devices.
- Wall Street thinks AI-driven hyperscaler capital spending may exceed $520B in 2026.
- The 10th most populous U.S. state, Michigan, just approved a contract to provide up to 1.4 GW for a single data center.
- Large power transformers required to support data center power demand are facing lead times exceeding two years.
Against that backdrop, Ethernet’s presence in data centers continues to swell, with switch orders doubling between 2022 and 2025. Ethernet has moved ahead of InfiniBand in AI back-end networking, a trend that looks to be unstoppable at this point. Vendors are increasingly targeting scale-up networks previously dominated by proprietary interconnects, while 1.6-Tb/s switches are expected to ship in volume in 2026. And this may even end up being the year that co-packaged optics (finally!) gain ground.
On the standards front, IEEE 802.3 expects to complete IEEE 802.3dj, covering 200 Gb/s, 400 Gb/s, 800 Gb/s, and 1.6 Tb/s, by late 2026. At the same time, a 400-Gb/s/lane Signaling Call For Interest (CFI) is already scheduled for March.
There’s active debate surrounding modulation approaches, but assuming PAM-6 for the moment and ignoring coding overhead, the math quickly becomes sobering. PAM-6 provides roughly 2.5 bits per symbol, implying symbol rates on the order of 160 GHz for 400G per lane. My friends in the SerDes and connector space tell me that at a wavelength of 0.12 mm, board and component design can get challenging pretty fast.
In other news, Ethernet’s growth remains broad-based:
- The enterprise switch market is expected to exceed $30B in 2026.
- The industrial Ethernet market is expected to surpass $12B in 2025, with compound growth greater than 7% through 2032.
- Automotive Ethernet is projected to easily cruise on by the $3.3B mark in 2025 to $29.4B and a CAGR of more than 24% by 2035.
So, what’s the bottom line? Ethernet is on the cusp of unprecedented growth, thanks especially to AI data center networks. Simultaneously, it remains the linchpin of enterprise, mobile, and home networking, with steady — if not vigorous — expansion across all three. It’s also extending laterally into major segments such as industrial automation and automotive systems, while taking flight in emerging markets and applications, such as drones and spacecraft.
Never bet against Ethernet.
About the Author

David J. Rodgers
Ethernet Alliance President and Events & Conferences Chair, Ethernet Alliance
David J. Rodgers is a 35+ years industry professional, primarily focused on the Test and Measurement market. He is the Ethernet Alliance’s President and Events & Conferences Chair. His experience encompasses a comprehensive background in business and program management, and product development of serial protocol test and measurement solutions. He possesses wide-ranging serial communications protocol and interconnect validation experience. He’s most recently concentrating on deploying and marketing a broad range of high-speed serial analysis test and measurement products.
David currently represents EXFO for High-Speed electro-optical Test Technologies including Ethernet and Fibre Channel in various protocol industry groups, including the IEEE and T11 standards bodies and the Ethernet Alliance and the Fibre Channel Industry Association. He’s an original member of the USB Implementers Forum and one of the pioneer marketers of USB protocol analyzers.

Peter Jones
Chair, Ethernet Alliance
Peter Jones is the chair of the Ethernet Alliance. He’s a Distinguished Engineer in the Cisco Networking HW team, working on system architecture and standards strategy across the portfolio. While at Cisco, he has been a major contributor to the Catalyst switching product line, including the Catalyst 9000 series and the UADP ASIC family.
Peter has been active in IEEE 802.3 for several years, mostly working on BASE-T projects. He was the initial chair of the Ethernet Alliance Single Pair Ethernet technical subcommittee, and was Chair of the NBASE-T Alliance from its inception until its merger with the Ethernet Alliance. He works on evolution of technology to add value to physical infrastructure and make technology consumable.