SmartSSD Melds FPGAs and Flash Memory
What you’ll learn
- What is a SmartSSD?
- What can an FPGA do in a SmartSSD?
- Will SmartSSDs replace conventional SSDs?
The new SmartSSD computational storage device (CSD) is a joint venture by Xilinx and Samsung (Fig. 1). It was one of many new products highlighted at this year’s Flash Memory Summit, which has become much more than a flash memory get-together. It covers all aspects of storage, including intelligent storage like the SmartSSD.
The 3.84-TB flash drive sports a Xilinx Kintex FPGA. The FPGA has 523K lookup tables (LUTs), and over 60% are available for acceleration firmware. The SmartSSD has already been put into action using compression algorithms, video transcoding, and search. It can support machine-learning (ML) applications, offloading host processors and reducing transfer overhead to an off-board ML accelerator.
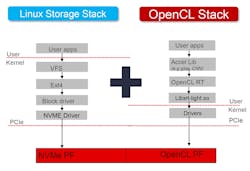
The FPGA has direct access to the non-volatile flash memory as well as 4 GB of DRAM, all fitting into a standard U.2 disk package. It looks like a standard NVMe SSD, but acts like two devices on the x4 Gen 3 PCI Express (PCIe) interface (Fig. 2). Two separate interface stacks are used on the host to communicate with the storage aspects as well as the computational aspects provided by the FPGA. OpenCL orchestration is already a standard component in the Linux device space.
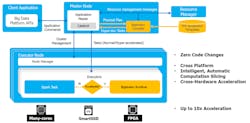
The standard interface enables developers to program the FPGA to handle a range of applications. For example, Bigstream’s solution provides acceleration of Apache Spark analytics with no code changes (Fig. 3). A single SmartSSD provides better performance than an 8-core/16-thread CPU with a regular SSD.
CTAccel’s video-processing acceleration support turns the SmarSSD into a smart streaming device, offloading the transcoding from the host. Eideticom’s computational storage solution provides transparent compression with a stacked file system. It can double or triple the storage capacity of the SmartSSD while adding only 80 µs of latency. The FPGA allows it to operate at 3 GB/s.
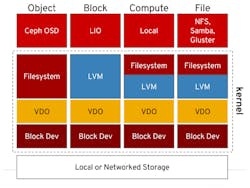
Xilinx Storage Services is another feature in the mix (Fig. 4). It supports the virtual data optimizer (VDO) layer provided by Linux storage support. Functionality like compression and encryption can be added to the stack. For example, dm-crypt implements encryption/decryption.
SmartSSDs may not replace conventional SSDs at this point due to additional cost, and not all storage applications need the functionality provided by a SmartSSD. Still, as the cost of these devices falls and as the functionality becomes more common, the SmartSSD is likely to displace conventional SSDs more frequently. That’s because it can provide features like compression and encryption in a selective fashion rather than the more limited fixed function support implemented in some SSDs.
About the Author
William G. Wong
Senior Content Director - Electronic Design and Microwaves & RF
I am Editor of Electronic Design focusing on embedded, software, and systems. As Senior Content Director, I also manage Microwaves & RF and I work with a great team of editors to provide engineers, programmers, developers and technical managers with interesting and useful articles and videos on a regular basis. Check out our free newsletters to see the latest content.
You can send press releases for new products for possible coverage on the website. I am also interested in receiving contributed articles for publishing on our website. Use our template and send to me along with a signed release form.
Check out my blog, AltEmbedded on Electronic Design, as well as his latest articles on this site that are listed below.
You can visit my social media via these links:
- AltEmbedded on Electronic Design
- Bill Wong on Facebook
- @AltEmbedded on Twitter
- Bill Wong on LinkedIn
I earned a Bachelor of Electrical Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology and a Masters in Computer Science from Rutgers University. I still do a bit of programming using everything from C and C++ to Rust and Ada/SPARK. I do a bit of PHP programming for Drupal websites. I have posted a few Drupal modules.
I still get a hand on software and electronic hardware. Some of this can be found on our Kit Close-Up video series. You can also see me on many of our TechXchange Talk videos. I am interested in a range of projects from robotics to artificial intelligence.