Optoisolators—also called optocouplers or photoisolators—are widely used to provide galvanic (ohmic) isolation of digital-signal inputs and outputs in industrial environments, as well as in other applications. The Toshiba TLP2363 is a high-speed (10 Mb/s) logic-level output photocoupler for the 24-V digital inputs often associated with programmable logic controller (PLCs) and other measurement and control equipment.
The device requires a supply current of just 4 mA and a threshold input current (IFHL) of 0.3 mA (minimum) and 2.4 mA (maximum) to ensure conformance to the digital input standard IEC 61131-2 type 1. The short propagation delay of just 80 ns is commensurate with high-speed systems and data rates.
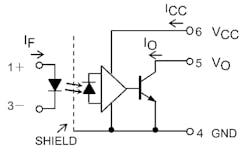
Although isolation voltage rating is partially a function of physical size and thus internal input/output physical separation as well as package-pin creepage and clearance, the TLP2363 offers a minimum isolation-voltage rating of 3750 Vrms. This despite being housed in a small, thin SO6 package with five actual pins (pin 2 is absent) and with a maximum height of 2.3 mm. By using the common six-pin optocoupler footprint, it can be a drop-in replacement for existing optocouplers from many vendors (see figure).
The TLP2363, which meets a long list of relevant regulatory standards, incorporates an internal Faraday shield to guarantee common-mode transient immunity of ±20 kV/µs and is rated for a wide operating temperature range of−40 to +105°C). The detailed, 18-page datasheet offers numerous min/max/typical values for key parameters as well as graphs defining performance across a range of factors.
About the Author

Bill Schweber
Contributing Editor
Bill Schweber is an electronics engineer who has written three textbooks on electronic communications systems, as well as hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. In past roles, he worked as a technical website manager for multiple topic-specific sites for EE Times, as well as both the Executive Editor and Analog Editor at EDN.
At Analog Devices Inc., Bill was in marketing communications (public relations). As a result, he has been on both sides of the technical PR function, presenting company products, stories, and messages to the media and also as the recipient of these.
Prior to the MarCom role at Analog, Bill was associate editor of their respected technical journal and worked in their product marketing and applications engineering groups. Before those roles, he was at Instron Corp., doing hands-on analog- and power-circuit design and systems integration for materials-testing machine controls.
Bill has an MSEE (Univ. of Mass) and BSEE (Columbia Univ.), is a Registered Professional Engineer, and holds an Advanced Class amateur radio license. He has also planned, written, and presented online courses on a variety of engineering topics, including MOSFET basics, ADC selection, and driving LEDs.