This Week in PowerBites: New Eval Kits and Ref Designs Plus GM Adapter to Speed EV Adoption
This article is part of the This Week in PowerBites Library Series.
What you’ll learn:
- A fresh crop of highly integrated motor controllers and motor-drive ICs is enabling rapid development of compact, energy-efficient motor systems for appliances, consumer goods, and industrial applications.
- Power MOSFETs and BJTs both benefit from advanced SMT packaging technologies that enable them to run cooler, supporting compact, power-dense designs.
- The rate of North American EV adoption is expected to benefit from GM’s recent announcement of the availability of adapters that will enable seamless connection with Tesla’s Supercharger stations.
Bill Pierce from EVInfo.net reports that General Motors is poised to offer access to more than 17,800 Tesla Superchargers for its customers, with the use of a GM-approved NACS DC adapter. The move is expected to help accelerate fast and convenient charging options for current and future EV drivers.
In addition to installing NACS-compatible charging ports on many of its new EVs, GM says that company-approved approved NACS DC adapters for vehicles equipped with older-style ports will soon be made available to customers in the United States, followed by availability for Canadian customers later this year.
With the addition of the Tesla Supercharger Network, GM customers will have access to more than 231,800 public Level 2 and DC fast chargers in North America. And, according to GM, that number will continue to grow as the carmaker and other companies continue their efforts to support the deployment of infrastructure in communities and heavily traveled corridors through its various charging collaborations.
Click here to read the full story at EV Info. Additional information about GM’s public charging options is available on GM’s public charging webpage.
Compact Intelligent Power Device for BLDC Motor Drives up to 3 A/600 V
Toshiba Electronics’ latest intelligent power device (IPD) was developed for space-constrained brushless DC (BLDC) motor-drive applications such as air conditioners, air purifiers, and pumps. Suitable for sine-wave drive applications, the TPD4165K offers an increased maximum output current of 3 A—over the 2-A rating of Toshiba’s earlier IPDs such as the TPD4163K or TPD4164K.
The TPD4165K incorporates several important safety features including overcurrent, undervoltage, and thermal shutdown, and supports current sensing using either a three-shunt or single-shunt resistor circuit. In addition, an external signal can be applied to the SD pin to control the behavior of the output stage. The DIAG output pin provides the status of the safety conditions.
The new device’s absolute maximum voltage rating (VBB) has been increased by 20%, to 600 V, to enhance long-term reliability in regions where mains supply voltages experience wide fluctuations.
Designers can freely access a reference design for a sensorless BLDC motor-drive circuit based on the new TPD4165K and Toshiba’s TMPM374FWUG microcontroller with vector control engine capability. The reference design data can be downloaded from the company’s website.
The TPD4165K is housed in a through-hole HDIP30 package. It has a 21% smaller footprint than the DIP26 package used for many of Toshiba’s previous products, simplifying the design process for challenging space-constrained applications. The device measures just 32.8 × 13.5 × 3.525 mm.
Click here to learn more about the new IPD.
HV Power Stage Pairs with Space-Efficient Eval Board for Smaller, Tougher Motor Drives
Created to accelerate development of compact energy-efficient and reliable fans and pumps, STMicroelectronics’ PWD5T60 is a three-phase driver IC that comes with a companion evaluation board to support flexible control strategies.
The PWD5T60 integrates a gate driver and six power MOSFETs with an RDS(on) of 1.38 Ω, capable of supporting applications up to 500 V. The propagation delays of high- and low-side MOSFETs are closely matched, which eliminates cycle distortion and maximizes flexibility to set the operating frequency for optimum response and energy efficiency.
The driver also includes zero-drop bootstrap diodes, further contributing to its high level of integration. This enables the device to achieve an outstanding energy-to-area rating while requiring only 30% of the board area needed to implement an equivalent driver built with discrete components.
Designers can easily explore applications for the controller using the EVLPWD-FAN-PUMP evaluation board. It combines the PWD5T60 with an STM32G0 microcontroller (MCU) that can handle field-oriented control (FOC) or six-step control of permanent-magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) and brushless DC (BLDC) motors.
The board features a power-supply stage to generate 12- and 3.3-V supply voltages for the application and can be quickly configured to support either single- or three-shunt sensing. It has a wide input supply voltage range from 9 to 20 V for optimum flexibility, while CMOS/TTL-compatible logic inputs down to 3.3 V simplify interfacing with a host controller.
Featuring on-board bus-voltage sensing, the EVLPWD-FAN-PUMP board makes full use of the PWD5T60’s protection features. These include undervoltage lockout (UVLO) for each bootstrap section, cross-conduction prevention with interlocking and pre-programmed default deadtime, and a smart shutdown feature that uses a comparator for fast-acting overcurrent prevention.
The PWD5T60, in full production, comes in a compact 12- × 12-mm VFQFPN package that’s only 0.95 mm high. Pricing is from $3.28 for orders of 1,000 pieces.
The EVLPWD-FAN-PUMP evaluation board is available now from the eSTore at the budgetary price of $102.00. The board delivers plug-and-play convenience, leveraging FOC and six-step control firmware in the X-CUBE-MCSDK motor-control software development kit available free of charge from the company’s site.
Customizable 240-W USB PD Eval Board Supports Unlimited Ports
A new evaluation board from Eggtronic enables engineers to experiment with an easily customizable reference design that reduces the size, cost, and development time for USB PD 3.1 applications. It delivers up to 240 W while supporting high efficiency and ultra-fast charging.
The SmartEgg 240-W PD 3.1 board has a peak efficiency above 95% and operates at over 90% efficiency from light load to full load. A single stage that combines zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) power factor correction (PFC) and quasi-forward isolated regulation significantly reduces both its bill of materials (BOM) and the size of key components (including storage capacitors and magnetics), as compared to traditional PFC+LLC and PFC+Asymmetric Half-Bridge (AHB) architectures.
The result is a platform that delivers light-load energy savings of up to 50%, achieves a power density of 21.9W/in.3 (1.34W/cm3) to support extremely compact charger designs, and, most importantly, dramatically reduces BOM cost.
Based on the SmartEgg AC/DC architecture, the new evaluation board incorporates the company’s proprietary EPIC 2.0 mixed-signal, low-power controller ICs and features built-in protection against overpower, overvoltage, overtemperature, short circuits, and brownouts. EPIC is based on a 32-bit RISC-V core and a rich set of high-performance digital and analog peripherals. It incorporates a flexible internal structure that supports multiple independent control loops of both standard and proprietary power-conversion architectures.
Initially configured as a dual-port module, the SmartEgg 240-W PD 3.1 EVB can be quickly modified to support any number of charging ports. This flexibility is made possible by the EPIC 2.0 controller, which can be configured via I2C communication to support many slave buck converters, each acting as a standalone port.
Because the master EPIC IC on the secondary side adjusts all of the charging cases by distributing the power needed to each port or allocating the full power to a single port, the power-sharing behavior can be quickly and easily customized.
SiC MOSFETs Bring Enhanced Robustness and Efficiency to 400-, 800-V EV Apps
Navitas Semiconductor recently announced its new portfolio of third-generation, automotive-qualified SiC MOSFETs in D2PAK-7L (TO-263-7) and TOLL (TO-Leadless) surface-mount (SMT) packages. According to the company, its proprietary “trench-assisted planar” technology provides excellent performance over temperature and delivers high-speed, cool-running operation for electric-vehicle (EV) charging, traction, and DC-DC conversion.
With case temperatures up to 25°C lower than conventional devices, Gen-3 Fast SiC offers an operating life up to 3X longer than alternative SiC products for high-stress EV environments.
Gen-3 Fast MOSFETs are optimized for the fastest switching speed and highest efficiency, and they support increased power density in EV applications such as AC compressors, cabin heaters, DC-DC converters, and on-board chargers (OBCs). Navitas’ dedicated EV Design Center has demonstrated leading-edge OBC system solutions of up to 22 kW with 3.5-kW/liter power density, and over 95.5% efficiency.
400-V-rated EV battery architectures are served by the new 650-V Gen-3 Fast MOSFETs, which feature RDS(on) ratings from 20 to 55 mΩ. The 1,200-V version ranges from 18 to 135 mΩ and is optimized for 800-V systems.
Both 650- and 1,200-V ranges are AEC Q101-qualified in the traditional SMT D2PAK-7L (TO-263-7) package. For 400-V EVs, the 650 V-rated, surface-mount TOLL package offers a 9% reduction in junction-to-case thermal resistance (RTH,J-C), 30% smaller PCB footprint, 50% lower height, and 60% smaller size than the D2PAK-7L. This enables very high-power-density solutions, while minimal package inductance of only 2 nH enhances fast-switching performance and minimizes dynamic package losses.
The automotive-qualified 650- and 1200-V G3F SiC MOSFET family is available immediately for purchase.
Classic Power BJTs Now Available in Space- and Energy-Efficient DFN2020D-3 Packages
A new packaging option is now available for Nexperia’s portfolio of power bipolar junction transistors (BJTs): Initial products in this new series include 10 standard and 10 automotive-qualified products in DFN2020D-3 packaging. These devices, available in 50- and 80-V ratings, support current ranges from 1 to 3 A in NPN and PNP polarity.
DFN2020D-3 packaged devices provide significant space savings versus their leaded counterparts. For example, there’s an 80% reduction in board space when compared to SOT89 and a 90% reduction compared to SOT223. The DFN2020D-3 package also features side-wettable flanks to enable automated optical inspection (AOI) of solder joints, thus ensuring improved robustness and reliability.
In addition to general-purpose transistors, Nexperia also released a series of low VCEsat devices, like the PBS5350PAS-Q. Combining exceptionally low saturation voltage and high current gain, they can help to improve the energy efficiency of many power-supply applications.
With this release, the company now offers the majority of its power BJTs in DFN packaging for designers looking for a space- and energy-efficient alternative to older SOT223 and SOT89 packages.
Nexperia supports engineers working with bipolar junction transistors with the BJT Application Handbook, a practical, comprehensive, and up-to-date reference work written by engineers for engineers. It provides a better understanding of bipolar transistors, their fundamentals, thermal considerations, and application insights.
To learn more about Nexperia’s bipolar transistors, click here.
240-V/1-kA Bidirectional Power TVS Diode Now Comes in Surface-Mount Package
Bourns introduced the industry’s first 240-V/1-kA bidirectional power TVS (PTVS) diode available in a surface-mount package. Offering one of the highest power densities in its class, the Model PTVS1-240C-M PTVS diode uses advanced silicon processing technology to achieve high voltage-handling capabilities, while its surface-mount packaging suits it for applications that require high reliability and a compact form factor.
Offering 1-kA surge handling capability under 8/20-µs test conditions, the PTVS1-240C-M targets a broad variety of systems that employ high-voltage DC bus architectures. These systems commonly experience high current switching transients and dynamic load behaviors that require snubbing or protection of bus-powered subsystems. This includes industrial power systems, motor controllers and inverters, solar inverters, battery energy storage systems, and factory automation.
The PTVS1-240C-M PTVS diode is a low-leakage device consuming only 10 µA in standby while delivering a maximum breakdown voltage of 295 V, repetitive standoff voltage of 240 V, and precise clamping voltage of 340 V. Under 10/350-µs conditions, this device is rated for 200-A peak current, and its voltage breakdown sensitivity over temperature is an extremely linear 0.1%/°C.
The surface-mount package offers a significantly reduced PCB footprint and lower inductance design advantages compared to traditional through-hole-mounted power TVS diodes.
The Bourns Model PTVS1-240C-M, available now, is UL497B certified and meets IEC 61000-4-5 standard specifications. For additional information, go here.
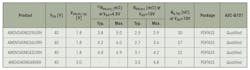
40-V MOSFETs Optimized for Automotive Motors and Low-Power Control Systems
Magnachip Semiconductor added four 40-V MOSFETs to its Magnachip eXtreme Trench Medium Voltage (MXT MV) product family. All four devices, housed in compact power dual flat no-Lead (PDFN) 33 packages, are rated for use in automotive applications, including autonomous-driving and infotainment systems.
Compared to earlier 40-V MOSFET products packaged in PDFN56 style, the devices’ PDFN33 packaging reduces their PCB footprint by over 60% and weight by approximately 75%. This makes them even more suitable for automotive motors and low-power control systems, where performance, fuel efficiency, and space flexibility are crucial.
Among these new products, three models—AMDV040N029LVRH, AMDV040N036LVRH, and AMDV040N042LVRH—are distinguished by their low gate-threshold voltage of 1.8 V. The gate-threshold voltage determines the point at which the MOSFET switches from an off-state to an on-state. A lower threshold voltage reduces the energy required to operate the MOSFET, thereby decreasing the overall power consumption of the system.
The key specifications of the four new automotive 40-V MXT MV MOSFETs are as follows:
The AL58221, a new 12-channel, constant-current LED driver developed by Diodes Inc., is suitable for use in indoor and outdoor LED video signage and displays, variable messaging signs (VMS), architectural and decorative LED lighting systems, and LCD backlighting.
The driver features 12 open-drain outputs that are rated to 24 V and sink up to 60 mA of high-accuracy current with a fast transient response. The channel-to-channel LED current accuracy is typically ±1% and the regulated output current tolerance is ±0.1%. Operating over a 3- to 5.5-V input, the driver uses adaptive pulse density modulation (APDM) to help mitigate non-ideal IOUT distortion and enhance visual refresh rates for improved performance.
The driver’s LED current is set by three external resistors (for RGB master setting), with each channel’s average output current being programmed independently via its digital interface. It features a 10-MHz, double-edge-triggered, data clock input that reduces EMI. The device’s two-wire serial interface sends grayscale data to the function-control registers that store the configuration information. It controls grayscale resolution and clock frequency, current output waveform selection, and internal-latch function.
The AL58221 uses APDM to increase the visual refresh rate of >1,000 Hz at 16-bit and >256 kHz at 8-bit grayscale. This technique reduces flicker and provides output-current bilateral processing for EMI reduction. A clock duty recovery technique with pulse retiming supports a longer-distance connection. Its two-wire serial interface also enables cascading applications for up to 1,030 devices.
For applications requiring higher resolution or larger display areas, the recently introduced AL58263 is a 16-channel device with 16-bit PWM grayscale dimming control.
The AL58221 and AL58263 come in the thermally enhanced TSSOP-24EP (Type A1-B) package; pricing is $0.37 and $0.47, respectively, in 1,000-piece quantities.
High-Efficiency Reference Design for 3,300-W Bridgeless Totem-Pole Inverter Has Low Parts Count
Infineon introduced a fully customizable reference design for a bridgeless totem pole inverter that’s capable of delivering up to 3,300 W. The EVAL_3K3W_TP_SIC_TOLL board is a full system solution utilizing the company’s power semiconductors, drivers, and microcontrollers.
The board boasts a digitally controlled SiC-based bridgeless totem-pole topology, well-suited for high-end applications that demand exceptional efficiency and power density. The totem-pole design enables simplicity, reduces component count, and optimally utilizes the PFC inductor and switches, allowing for high power density at limited system cost.
The compact design offers high efficiency (98.9% at 1650 W, 50% load), low component count, and high energy density (80 W/in.³).
Applications include:
Read more articles in the This Week in PowerBites Library Series.