Voltage Conversion in Four Quadrants (.PDF Download)
While simple voltage converters can generate a fixed output voltage from an input voltage, this behavior isn’t sufficient in certain applications. An example is the control of a voltage node that has capacitors connected to it. These capacitors may be charged to any voltage. If they need to be brought to a lower voltage, they have to be partially discharged. Thus, in such an application, a power supply must be able to source or sink current as required.
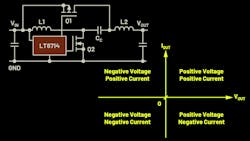
Such a converter is called a four-quadrant dc-dc converter. For applications of this type, a power supply can be used with an output discharge function. It can quickly discharge output capacitors. Figure 1 shows such a function for a step-down switching regulator. Here, switch S2 is switched on for a lengthy period after the switching action of the buck converter is switched off and the output capacitor is discharged.