Supervisory IC Targets and Eliminates Power-Good Glitching in Low-Voltage Circuits
Experienced engineers know that transient situations can be the most challenging, frustrating, and erratic of occurrences. It may involve the restarting of a data link after link-loss, or simply bringing up a system’s power rails where the supervisory-based reset decision has to be “just right” and not issued prematurely.
Conventional supply supervisor ICs often have difficulty controlling their reset output state when the input voltage rail (VCC) has a very low nominal value—an increasingly common design scenario. That can lead to inconsistent circuit “startup” performance and extended debug sessions.
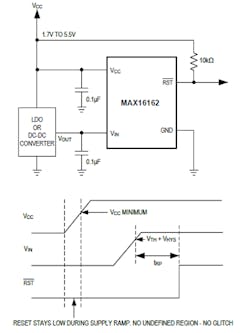
Such a situation is addressed by the MAX16161 and MAX16162, a similar pair of ultra-low-current, single-channel supply-rail supervisors from Maxim Integrated Products (see figure). These glitch-free devices monitor the supply voltage and assert a reset when that input voltage falls below the reset threshold. After the monitored voltage rises above the factory-set threshold voltage, the reset output remains asserted for the reset timeout period and then de-asserts. As a result, the processor using that rail can finally leave its reset state and begin normal operation.
This action is in contrast to the characteristics of conventional supervisors, which are unable to reliably control the reset line’s output state when VCC is very low. The MAX16161/MAX16162 reset output is guaranteed to remain asserted until after a valid VCC is reached. This is especially important to prevent the situation of low-voltage cores leaving their reset state during power-up or power-down. It also improves performance when using the MAX16161/MAX16162 as basic power-supply sequencers, because the devices will not cause a transient enable of a downstream power supply due to output glitches.
The differences between the MAX16161 and MAX16162 are modest but noteworthy. The MAX16161 features a manual reset (MR) debounce input that asserts a reset when it receives an appropriate input signal, which may be either active-low or active-high (depending on the user-selected option) and has threshold-voltage options of 1.7 to 4.85 V. The MAX16162 has no such MR input; instead, it maintains separate VCC and VIN pins, supporting threshold voltages from 4.85 V down to 0.6 V.
Typical quiescent current is just 825 nA for these ICs, which are priced at for $1.19 (1,000 pieces). They’re specified over the −40 to +125°C temperature range and are housed in 1.06- × 0.73-mm, 4-bump WLP and 4-pin SOT23 packages. The comprehensive 20-page datasheet provides critical maximum/minimum specifications as tables and graphs, and EE-Sim models are available to support their design-in simulation.