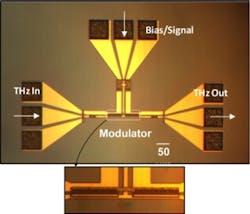
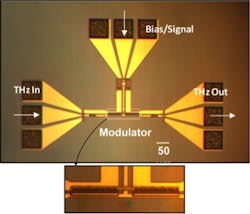
Tufts engineers develop modulator to help fill the terahertz gap
Engineers at Tufts University are looking to fill the terahertz gap—the band of frequencies between microwaves and infrared for which practical applications remain elusive. The engineers have invented a chip-sized modulator that operates at terahertz frequencies at room temperature with low drive voltages (less than 2 V) and zero DC power.
Measurements show the modulation cutoff frequency of the new device exceeded 14 GHz, indicating its potential for modulation of terahertz waves, according to a paper published online today in Scientific Reports.1
“This is a very promising device that can operate at terahertz frequencies, is miniaturized using a mainstream semiconductor foundry, and is in the same form factor as current communication devices,” said Sameer Sonkusale, Ph.D., of the Nano Lab, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Tufts University, and the paper’s corresponding author. “It’s only one building block, but it could help to start filling the THz gap.”
The device works through the interaction of confined THz waves in a slot waveguide with tunable, two-dimensional electron gas. The prototype device operated within the frequency band of 0.22 to 0.325 THz, which the engineers chose because it corresponded to available experimental facilities. The researchers say the device would work within other bands as well.
The authors write, “Applications of using THz radiation cover broad areas including material identification, imaging, wireless communications, [and] chemical and biological sensing.”
They add, “…existing solutions for terahertz modulation are limited to free space propagation of quasi-optical signals, which may be ideal for THz spectroscopy and imaging, but not really suitable for THz communication, which requires modulators be integrated with other components such as amplifiers and detectors on a single chip to enable realization of integrated THz transmitter and receiver systems.”
Reference
1. Sing, P.K., and Sonkusale, S., “High Speed Terahertz Modulator on the Chip Based on Tunable Terahertz Slot Waveguide,” Scientific Reports, published online Jan. 19, 2017. DOI: 10.1038/SREP40933.
About the Author

Rick Nelson
Contributing Editor
Rick is currently Contributing Technical Editor. He was Executive Editor for EE in 2011-2018. Previously he served on several publications, including EDN and Vision Systems Design, and has received awards for signed editorials from the American Society of Business Publication Editors. He began as a design engineer at General Electric and Litton Industries and earned a BSEE degree from Penn State.