What’s the Difference Between Lateral and Vertical Power Delivery? (Download)
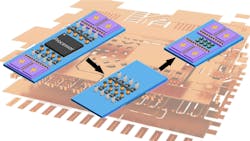
Powering a 1,000-A AI accelerator core that runs on less than 1 V is one of the hardest engineering problems faced by power designers today. However, this represents just the beginning of the challenge. Around the main AI accelerator core, there are 40 to 50 secondary power rails for every single primary power rail. These secondary power rails supply power for memory, I/O, and other important functions.
The power distribution network (PDN) for the entire system poses significant difficulties. As current is forced through the resistance present in this network, power losses inevitably add up. These I2R losses can waste more than 20% of the processor’s thermal design power (TDP). When power losses are this high, the traditional lateral power delivery (LPD), where the DC-DC converters sit next to the processor on the same side of the PCB, reaches its limits.