Pseudo-SLC NAND Improves Critical-App Reliability—While Cutting Costs
- What is pseudo SLC (pSLC) NAND?
- How pSLC fits in embedded applications.
- Cost and reliability tradeoffs of using pSLC.
Noted for its high performance, reliability, compact form factor, low power consumption, and ability to work over an extended temperature range, single-level-cell (SLC) NAND stands apart as a cornerstone NAND flash technology. Given its multiple positive attributes, it's no surprise that SLC NAND is finding a welcome home in a variety of Internet of Things (IoT), automotive, and emerging embedded applications, as well as other applications that require long life and/or high reliability.
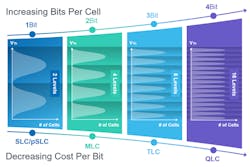
SLC NAND offers an ideal balance between cost and performance to store boot and small to medium OS code for many applications (see figure). Yet, for high-density storage applications, it presents a major drawback: cost. In fact, the technology can often be prohibitively expensive.
Attributes and Characteristics
Until recently, designers faced a serious dilemma. One could take a cautious approach and turn to durable, yet expensive, SLC NAND, or opt for a lower cost, yet also less reliable and slower performing, multi-level-cell (MLC) and triple-level-cell (TLC) NAND. Today, however, there's a far better alternative: pseudo-SLC (pSLC) NAND technology.
With pSLC NAND, the likes of MLC NAND, TLC NAND, and quad-level-cell (QLC) NAND can be used in an approach that lowers the number of bits stored in each cell to just one. It's important to note that MLC NAND natively stores two bits per cell, TLC NAND stores three bits per cell, and QLC NAND accommodates four bits per cell. Reducing the number of stored bits in each cell to only one increases the NAND's lifespan and reliability while lowering cost—a win-win proposition.
pSLC NAND operates in a manner similar to SLC NAND, but with fewer program erase cycles, which makes it a cost-effective alternative to SLC NAND. pSLC is also attractive from the standpoint that it uses the latest 3D technology.
Although pSLC NAND technology shrinks MLC NAND memory capacity by 50%, TLC capacity by 66.6%, and QLC NAND capacity by 75%, it still manages to deliver a significantly lower cost-per-bit than ordinary SLC NAND thanks to its higher cell density. Furthermore, pSLC NAND boosts reliability, performance, and endurance attributes to levels closely comparable to costlier SLC NAND technology. For most industrial applications, though, pure SLC NAND devices still provide the best reliability. Besides its rapid read speed, pSLC NAND also offers up to 10X greater endurance than TLC NAND.1
On the downside, pSLC NAND devices share an unfavorable characteristic with their MLC NAND counterparts, namely small cells (when compared to other NAND technologies). This means that pSLC NANDs are far more prone to corruption, cell crosstalk, read disturb errors, and data-retention issues. In addition, since pSLC NAND limits data storage per cell, it doesn’t have the device architecture benefits offered by standard, yet costlier, SLC NAND.
When all of the price, implementation, and performance factors are considered and evaluated, it becomes clear that pSLC NAND technology provides both a long-term service life and great cost value. Although pSLC NAND adopters should realize that they’re not going to obtain the same high reliability levels provided by pure SLC NAND, the newer technology's lower cost, yet still generally high reliability characteristics, make it an optimal choice for a wide range of storage applications.
Cost Considerations
Lower cost is usually the primary reason for turning to pSLC NAND. While pSLC NAND adopters are never going to achieve the high reliability of pure SLC NAND, there's a price reliability/balance, or tradeoff, that always comes into play.
When considering the use of a new storage technology, SLC NAND usually wins this contest. On the other hand, if a project's primary goal is simply achieving pure cost per gigabyte—and maximizing overall storage capacity, reliability, and durability are all relatively unimportant—TLC still exists as the lowest-price option.
Use Cases
Today's NAND market is primarily driven by the growing demands of data-center technology providers, smartphone manufacturers, and other high-density device customers. Such buyers seek high-density NAND solutions that can provide storage at the lowest possible cost per gigabyte. On the other hand, for developers focusing on lower-density applications that require a NAND with strong reliability and endurance characteristics, the only realistic options are either pSLC NAND or costlier SLC NAND.
In the case of SSD applications, they typically use a combination of pSLC partitions along with MLC/TLC mode. pSLC NAND offers a solution that outweighs others for storage applications that demand high reliability, durability, and the ability to completely maintain and protect code and data integrity.
Overall, pSLC NAND is a good fit for applications that require SLC NAND-level endurance but can't tolerate the high-cost burden associated with pure SLC NAND. In the battle between flash attributes and cost, pSLC NAND offers a better compromise of reliability, speed, and endurance when compared to pure SLC NAND, with only a few modest drawbacks. Remember, too, that high-density SLC NAND is becoming increasingly hard to find, a challenge that designers must consider when selecting an appropriate NAND technology.
Specific pSLC NAND applications include high-endurance SD cards (cards used by surveillance cameras, for example), network cards, and small SSDs. In fact, any application that must reliably function in an environment with extreme high or low temperatures can benefit from pSLC NAND technology.
Particularly effective areas for pSLC NAND technology include devices and systems that routinely experience extreme environmental conditions, such as in cell tower equipment, outdoor signage, industrial sites, outside IoT devices, and even space vehicles and satellites. pSLC partitioned NAND is also well-suited for use in automobiles, trucks, trailers, motorcycles, and scooters, as well as all types of aircraft and seagoing vessels—any type of moving vehicle that's likely to experience extreme internal and external temperature conditions.
Conclusion
It's important to remember that while pSLC NAND has arrived as a breakthrough storage technology, it will never completely eliminate the need for pure SLC NAND devices. Application, performance, and reliability requirements will always stand as the benchmarks that ultimately determine which SLC NAND solution should be used.
Brian Kumagai is the Director of the Memory Business Unit at KIOXIA America Inc.