Vision-Language-Action Model Opens Level 4 Frontier for Autonomous Driving
Safely achieving end-to-end autonomous driving is the cornerstone of Level 4 autonomy and the primary reason it hasn’t been widely adopted. The main difference between Level 3 and Level 4 is the requirement for human intervention.
In a Level 3 vehicle, the driver must be available to take over when prompted. In a Level 4 vehicle, no human intervention is required within the defined operational boundaries.
In line with the industry moving toward scalable, AI-driven Level 4 solutions, NVIDIA just released new open-source software dubbed Alpamayo-R1 (AR1), aimed at speeding up the development of self-driving cars. The software uses generative AI and large language models (LLMs), an AI system trained on massive amounts of text data to understand and generate human-like language, to enable self-driving systems to solve complex driving situations with humanlike reasoning and adaptability.
Open-Source Vision-Language-Action AI Model
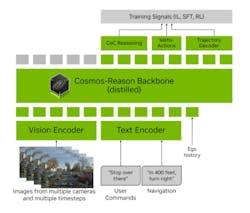
Alpamayo-R1 (AR1) is best described as an open-source "vision-language-action" AI model designed to help self-driving cars "think aloud" as they make driving decisions. Visual language models can process both text and images together, allowing vehicles to “see” their surroundings and make decisions based on what they perceive.
AR1 accomplishes this by breaking down a scenario and reasoning through each step. It considers all possible trajectories and then uses contextual data to choose the best route, making it capable of handling intersections crowded with pedestrians, double-parked vehicles, or lane closures. NVIDIA hopes that this type of reasoning model will give autonomous vehicles the “common sense” to better approach nuanced driving decisions like humans.
The semiconductor company announced AR1 at NeurIPS, the 39th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems in San Diego Dec 2-7. NVIDIA claims this is the first vision-language-action model focused on autonomous driving.
Real-Time Route Planning
Alpamayo, named for a mountain peak in Peru, is said to “think” as it plans its route. By tapping chain-of-thought reasoning, the autonomous vehicle can then interpret nuanced and unpredictable real-world conditions — such as an upcoming lane closure or a vehicle parked in a bike lane or unpredictable human behavior — in real-time.
In this way, it can translate what its sensors see on the road into a description using natural language. A secondary benefit is AR1 can explain to design engineers why it took certain actions and use that information to plan future trajectories.
Making the World Robotaxi-Ready
NVIDIA’s end-to-end platform for autonomous vehicles incorporates AI-powered computing hardware such as the NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Hyperion 10, software, and data center solutions for training. Also in the mix are simulation tools such as Omniverse, a platform that runs on existing operating systems like Windows and Linux for testing and validation.
The company has partnered with automotive companies, including GM, Lucid, Mercedes-Benz, Rivian, Stellantis, Toyota, and Volvo, to create Level-4-ready autonomous vehicles and teamed up with Uber to build a network of self-driving cars.
Uber will begin scaling its global autonomous fleet starting in 2027, targeting 100,000 vehicles. It will be supported by a joint AI data factory built on the NVIDIA Cosmos platform.
Open access is central to NVIDIA’s strategy. AR1, built on NVIDIA Cosmos Reason, can be customized by researchers for non-commercial applications. Beyond AR1, NVIDIA’s Cosmos platform offers a suite of tools for physical AI development. These include LidarGen, which generates LiDAR data for AV simulation.
At the same time, NVIDIA, Aurora, and Volvo Autonomous Solutions are extending Level 4 autonomy to long-haul freight powered by the NVIDIA DRIVE platform. Their next-generation systems, built on NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Thor, will accelerate Volvo’s upcoming L4 fleet, extending the reach of end-to-end NVIDIA AI infrastructure from passenger mobility to long-haul freight.
DRIVE AGX Hyperion 10
The NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Hyperion 10 production platform features the NVIDIA DRIVE AGX Thor system-on-a-chip; the safety-certified NVIDIA DriveOS operating system; a fully qualified multimodal sensor suite including 14 high-definition cameras; nine radars, one LiDAR and 12 ultrasonic units; and a qualified board design.
At the core of DRIVE AGX Hyperion 10 are two DRIVE AGX Thor in-vehicle platforms based on NVIDIA Blackwell architecture. Each delivers more than 2,000 FP4 TFLOPS of real-time compute. DRIVE AGX Thor fuses diverse, 360-degree sensor inputs and is optimized for vision-language-action models and generative AI workloads. This leads to safe, level 4 autonomous driving backed by safety certifications and cybersecurity standards.