Advanced Power Conversion and Energy Management Solutions at TI
What you’ll learn:
- Semiconductors are central to the renewable-energy transition, enabling efficient conversion for solar, battery storage, and DC consumption.
- Single-stage power converters, using wide-bandgap devices like GaN FETs, are improving solar efficiency and reducing system size.
- Texas Instruments supports these innovations with reference designs, driving grid flexibility and robust energy management.
This first of a two-part Inside Electronics podcast series, guest-hosted by technology editor Andy Turudic of Electronic Design, features Henrik Mannesson, General Manager of Grid Infrastructure and Power Delivery Industrial Systems at Texas Instruments (TI). They discuss the evolving landscape of energy infrastructure with a focus on the pivotal role of semiconductors in the renewable-energy transition. All of the content in this pair of podcasts was an impromptu, no-holds-barred, first-time-ever meeting.
After introducing himself and his background, Henrik outlines the shift over the past decade from traditional electromechanical generation methods—such as synchronous generators in coal, nuclear, and hydro plants—to renewable sources, particularly solar, which has moved semiconductors to the center of energy-conversion technologies.
Henrik highlights the convergence of three key trends: the rise of DC-based solar generation, the growing importance of battery energy storage systems (BESS), and the increasing DC consumption by data centers and other digital infrastructure. All require efficient AC-DC and DC-AC conversion to integrate with legacy AC transmission grids.
A significant portion of Andy and Henrik’s talk centers on innovations in power-conversion topologies, specifically the emergence of highly efficient single-stage converters for residential and rooftop solar applications.
Traditional two-stage conversion (AC-DC followed by DC-AC) is being superseded by single-stage designs. They improve system efficiency by eliminating redundant conversion steps that compound each stage’s losses and by reducing passive component count and their associated losses. Henrik notes that these advances are enabled by wide-bandgap devices, such as GaN FETs, which offer low switching losses and support higher switching frequencies, further shrinking converter size and enhancing performance.
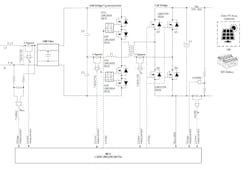
TI supports these developments in single-stage conversion with reference designs like the TIDA-010954 "cycloconverter” (see figure). It integrates maximum power point tracking (MPPT) and AC output regulation in a single conversion stage, streamlining residential solar inverter design.
Henrik also emphasizes the need for continued innovation in battery storage and real-time monitoring. These are areas where semiconductors will drive greater grid flexibility, higher renewable penetration, and more robust energy management as the transition to clean energy accelerates.
Please have a listen on your commute, lunch, break, or whenever you have a chance to safely spend about 15 minutes learning where the industry and market is headed in solar and battery electric storage systems. Also, check out Part 2 of this Inside Electronics podcast with Henrik and Andy. New episodes of the Inside Electronics podcast air every Tuesday, so feel free to add it to your lunch calendar.
>>Check out this TechXchange for more podcasts
About the Author
Andy Turudic
Technology Editor, Electronic Design
Andy Turudic is a Technology Editor for Electronic Design Magazine, primarily covering Analog and Mixed-Signal circuits and devices and also is Editor of ED's bi-weekly Automotive Electronics newsletter.
He holds a Bachelor's in EE from the University of Windsor (Ontario Canada) and has been involved in electronics, semiconductors, and gearhead stuff, for a bit over a half century. Andy also enjoys teaching his engineerlings at Portland Community College as a part-time professor in their EET program.
"AndyT" brings his multidisciplinary engineering experience from companies that include National Semiconductor (now Texas Instruments), Altera (Intel), Agere, Zarlink, TriQuint,(now Qorvo), SW Bell (managing a research team at Bellcore, Bell Labs and Rockwell Science Center), Bell-Northern Research, and Northern Telecom.
After hours, when he's not working on the latest invention to add to his portfolio of 16 issued US patents, or on his DARPA Challenge drone entry, he's lending advice and experience to the electric vehicle conversion community from his mountain lair in the Pacific Northwet[sic].
AndyT's engineering blog, "Nonlinearities," publishes the 1st and 3rd Tuesday of each month. Andy's OpEd may appear at other times, with fair warning given by the Vu meter pic.
Henrik Mannesson
General Manager, Grid Infrastructure and Power Delivery, Industrial Systems, Texas Instruments (TI)
Henrik Mannesson is general manager of Grid Infrastructure and Power Delivery, Industrial Systems, at Texas Instruments (TI).