The Robotic Revolution: Global Adoption Insights
What you'll learn:
- North American robotics usage trails behind global powers.
- Robotics filling labor gaps and boosting job satisfaction.
- Safety and security speculation in robotics.
- Growing concern around AI ethics and robotics governance.
Fueled by rapid technological advances, the global robotics market is expected to more than triple by 2030. Piling onto this trend, uncertainty brought forth by the current geopolitical landscape only intensifies the need for organizations to invest in efficiency-driving technology like robotics.
To embrace this shift, business leaders must prepare from both tactical and cultural standpoints. Recently, QNX surveyed technology decision-makers across the globe to gain a better understanding of current and anticipated robotics adoption.
North American Robotics Usage Trails Behind Global Powers
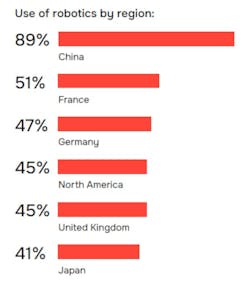
As a global superpower, North America falls behind other regions when it comes to robotics implementation. Currently, 45% of North American survey respondents say they utilize robotics within their organization, lagging the global average of 50%, and significantly trailing behind the APAC region with 65% implementation (including China at 89%) (see figure).
Although North America is currently lagging, 45% of organizations that aren’t yet utilizing robotics plan to do so within the next two years, compared to 47% globally. However, only 9% of North American decision-makers say they will take this action within the next year.
Some of the most significant factors influencing this group's decision to deploy robotics include advances in technology (88%), the ability to meet customer expectations (85%), cost reduction (85%), and improved safety (84%).
Trust in Robotics Remains High, But Comfort Hinges on Application Type
Globally, 77% of technology leaders trust robotics to perform essential industry functions. The most influential factors in this trust are improvements in risk reduction and safety (42%) as well as demonstrated reliability and performance (40%). Other considerations like accuracy, security, and regulatory compliance also play a role.
However, confidence in robotics varies based on the types of tasks with which they’re utilized. Organizations are more trusting of robotics to perform more repetitive tasks like assembly line work, material handling, and logistics and delivery, while tasks like customer service or medical procedures garner a leaner majority of confidence. It’s my belief that with additional experience and education focused on robotic technology, this sentiment will begin to shift.
Robotics Filling Labor Gaps and Boosting Job Satisfaction
Key industries like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing are turning to robotics to ease labor shortages. In North America, 66% of survey respondents shared that ongoing workforce shortages played a role in their decision to implement this technology. Apart from filling labor gaps, these decision-makers view robotics as a tool to improve overall job satisfaction with the ability to enhance work-life balance and reduce dangerous or repetitive functions.
To produce these types of results, it's critical for organizations to take a supportive and collaborative approach to robotics integration. Survey respondents overwhelmingly indicated (99%) that they provide training or upskilling programs to aid in working alongside or in conjunction with this technology. Along with providing the right training, almost all respondents (92%) indicated the importance of including employees in the conversation around workplace robotics integration.
Safety and Security Speculation
Security risks appear to be a point of contention when it comes to robotics implementation, with 58% of survey respondents expressing concern. This number is higher in North America (61%) and Europe (63%), but significantly lower in the APAC region (40%).
When it comes to safety, under one-third of respondents shared that their organization has experienced a dangerous scenario or safety risk while working alongside robotics. However, 89% believe the safety measures they have in place are effective at preventing such accidents.
Safety measures can include continual adherence to global standards as set forth by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which provides safety guidelines around the use of industrial robots within operations. These guidelines are continuously updated to reflect persistent changes. For example, the latest guidelines, ISO 10218-1, published this year outline standards specifically surrounding human-robot collaboration (cobots), which are becoming increasingly more prevalent.
Growing Concern Around AI Ethics and Robotics Governance
Even with international standards in place, respondent sentiment indicated room for improvement around robotics and AI governance. In North America, 72% of respondents believe that current government policies and regulations are somewhat adequate to very inadequate at addressing ethical implications within their industry. Only 17% of respondents cited current regulations as very adequate at addressing ethical implications.
Unclear guidelines on ethical use of AI and robotics is the most significant factor respondents indicated as contributing to the feeling of inadequacy, followed by a lack of comprehensive training and education programs.
Robotics are becoming not just a nice-to-have, but a need-to-have within organizations due to continuing economic uncertainty. With these advances and robotics industry growth, it’s critical for organizations to embrace adoption or risk being outpaced by competition.
About the Author
Winston Leung
Senior Manager, QNX
Winston Leung is a seasoned innovation strategist with over a decade of experience advancing technology and driving business development in public and private sectors across North America and Asia. Specializing in transformative industries like transportation and robotics, he has led initiatives in autonomous, connected, and electric vehicles, developing policies and strategies to support their adoption. Winston’s notable achievements include spearheading Canada’s first connected vehicle testbed and guiding go-to-market strategies for emerging technologies, including quantum, 5G, and more.
Currently a Senior Manager at QNX, Winston delivers strategies and thought leadership in functional safety, real-time performance, and reliability for embedded systems across robotics, medical, and transportation sectors. He has collaborated with international stakeholders, influenced government policies and driven startup success. Combining technical expertise with strategic insight, Winston is shaping the future of autonomous and robotics technologies through innovation and impactful leadership.