Chiplet-Based FPGA Tackles CXL
This article is part of the TechXchange: Chiplets - Electronic Design Automation Insights.
What you’ll learn
- What is an R-Tile?
- Why use an Embedded Multi-die Interconnect Bridge?
- Where does Agilex 7 fit in Intel’s FPGA landscape?
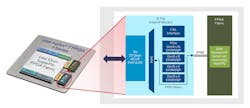
The Agilex FPGA family developed by Intel welcomes a new addition with the Agilex 7, which incorporates R-Tiles (Fig. 1). These chiplets are tied to an FPGA fabric using the Embedded Multi-die Interconnect Bridge (EMIB) chip-level interconnect. EMIB is a silicon-level interconnect that provides low-latency, high-speed connections between chiplets. These connections can be very wide compared to the more limited off-chip connections.
Agilex 7 supports PCI Express (PCIe) Gen 5.0 and Compute Express Link (CXL) 1.1/2.0. CXL is built on top of PCIe 5.0 and provides cache-coherent memory support. CXL provides a link between CPUs, GPUs, FPGAs, and other accelerators and is sponsored by the CXL Consortium.
Up to 4M logic elements and up to 485 Mb of memory is offered by the Agilex 7 (Fig. 2). There’s a 32-GB HBM2e option as well. The Agilex family supports options for dual- and quad-core Cortex-A processors, including the Cortex-A53. The Agilex 7 is the only one to currently support PCIe 5.0 and CXL. It also has the highest transceiver count but lacks the Direct RF support of the Agilex 9 family.
R-Tiles, F-Tiles, and More
The chip technologies used for different functionality, such as high-speed SERDES for communication, can be very different from the FPGA. Placing the components on different chiplets makes it possible to use the optimum technology to implement the components. EMIB can then be applied to link the different chiplets together.
The R-Tile used in the Agilex 7 family includes sixteen 32-Gb/s transceivers along with support for PCIe 5.0, CXL Type 1 and Type 2 with DCOH, and Type 3. It supports endpoint (EP) and Root Port (RP) as well as PIPE direct and transaction-layer bypass and switch options. CXL allows the Agilex 7 to be connected to Intel’s Xeon Scalable processors.
The Agilex 9 family utilizes F-Tiles. These have a dual-mode PAM4 and NRZ serial interface with up to 20 Physical Medium Attachments (PMAs) per tile. In addition, the Agilex 9 supports Direct RF, where the analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs) are also on chiplets tied to the FPGA fabric via EMIB.
CXL and Cloud Computing
The Agilex 7 support for CXL is significant, as it puts the FPGA on the same level as the processors, GPUs, and other CXL-capable accelerators like machine-learning accelerators as well as memory expansion. Essentially, all of the compute elements share a common memory environment.
CXL enables distribution of compute and storage elements. This disaggregation provides scalability and modularity when implementing a large cloud server environment that can be easily partitioned and managed.
CXL supports three protocols. CXL.io is a more powerful version of the standard PCIe 5.0 protocol used for peripherals. CXL.cache uses a request-response approach to host and devices, while the CXL.mem is designed for volatile and persistent memory. CXL 3.0 support will add pooling and direct peer-to-peer communication over the fabric.
Read more articles in the TechXchange: Chiplets - Electronic Design Automation Insights.
About the Author
William G. Wong
Senior Content Director - Electronic Design and Microwaves & RF
I am Editor of Electronic Design focusing on embedded, software, and systems. As Senior Content Director, I also manage Microwaves & RF and I work with a great team of editors to provide engineers, programmers, developers and technical managers with interesting and useful articles and videos on a regular basis. Check out our free newsletters to see the latest content.
You can send press releases for new products for possible coverage on the website. I am also interested in receiving contributed articles for publishing on our website. Use our template and send to me along with a signed release form.
Check out my blog, AltEmbedded on Electronic Design, as well as his latest articles on this site that are listed below.
You can visit my social media via these links:
- AltEmbedded on Electronic Design
- Bill Wong on Facebook
- @AltEmbedded on Twitter
- Bill Wong on LinkedIn
I earned a Bachelor of Electrical Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology and a Masters in Computer Science from Rutgers University. I still do a bit of programming using everything from C and C++ to Rust and Ada/SPARK. I do a bit of PHP programming for Drupal websites. I have posted a few Drupal modules.
I still get a hand on software and electronic hardware. Some of this can be found on our Kit Close-Up video series. You can also see me on many of our TechXchange Talk videos. I am interested in a range of projects from robotics to artificial intelligence.