Optimizing Power Systems for the Signal Chain (Part 2) (Download)
In Part 1 of this power-system optimization series, we examined how power-supply noise sensitivity can be quantified and how these quantities can be connected to real effects in the signal chain. The question was asked: What are the real noise limits to achieve superior performance of high-performance analog-signal-processing devices? Noise is just one measurable parameter in designing a power distribution network (PDN).
As noted in Part 1, a pure focus on minimizing noise can come at the cost of increased size, higher cost, or lower efficiency. Optimizing a PDN improves these parameters, while lowering noise to necessary levels.
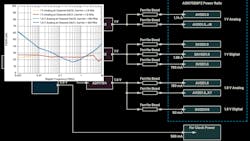
This article builds on the generalized overview of the effects of power-supply ripple in high-performance signal chains. Here, we dive deeper into the details of optimizing PDNs for high-speed data converters. We compare a standard PDN to an optimized PDN to see where gains can be made in space, time, and cost. Upcoming Part 3 will explore specific optimization solutions for other signal chain devices, such as RF transceivers.