How to Measure Current, Power for Improved System Monitoring (.PDF Download)
If you're seeking a way to measure current and power in a circuit, you need to know about current-sense amplifiers (CSAs). A CSA is a specialized op amp connected as differential amplifier with precision gain resistors on-chip. Its most common application is overcurrent protection in a wide range of products. These ICs make it easy to implement small, inexpensive overcurrent-protection features.
Current-Sense Amplifiers
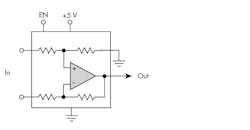
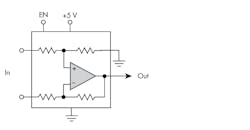
Figure 1 shows the basic circuit configuration. The op amp is connected as a differential amplifier. The input and feedback resistors are precisely matched to ensure good common-mode rejection. Resistor values determine the gain; multiple gain options are available. An enable (EN) input activates the circuit.
1. The current-sense amplifier is a precision differential op amp with on-chip gain resistors.
One key feature of a CSA is good support for common-mode voltages that are greater than the supply voltage. Some devices cover the −16- to +80-V range. Another important feature is ultra-low input offset voltage. With this error source kept low, greater measurement accuracy is possible. Good temperature stability is also a common characteristic achieved by integrating the gain resistors with the amplifier and related parts.