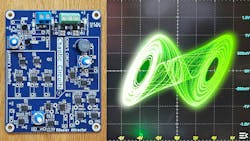
Circuits of Chaos: Building Lorenz, Chua, and Rossler Strange Attractors (Download)
To most people, "chaos" means confusion or randomness, but in mathematics, "mathematical chaos" refers to a deterministic behavior governed by precise nonlinear equations. A system is chaotic when it shows extreme sensitivity to initial conditions. In chaotic systems, the state doesn’t settle into a fixed point or predictable oscillation, but continuously evolves in a manner that’s highly sensitive to initial conditions and is hard to predict.
Designing and simulating electronic circuits that display chaotic behavior isn’t difficult. Chaos can be observed in virtually all aspects of life, including biology, geology, chemistry, finance, psychology, medicine, all branches of engineering and physics, economics, and countless other areas.